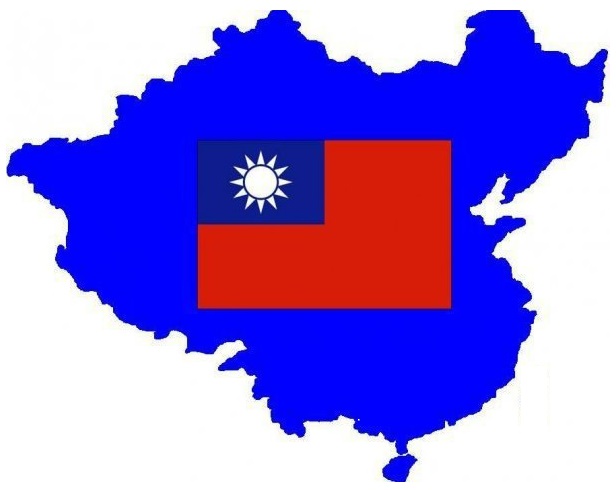
Examination of the Sovereign Territory claimed by the government of the Republic of China
|
|
|



|


|



|



|



|



|



|



|



|



Footnotes:
(1) See -- Red Star over China, by Edgar Snow, p. 110. https://www.taiwandc.org/hst-1624.htm
Alternate Source: China: The March Toward Unity, pp. 33-50. Published: Workers Library Publishers, 1937 [Original: China Weekly Review, November 14 and 21, 1936.] Online Version: Mao Zedong Internet Archive Public Domain: Marxists Internet Archive (2014). Internet -- https://www.marxists.org/reference/archive/mao/works/1936/11/x01.htm
(2) According to the ICRC website, the Republic of China ratified the 1907 Hague Convention (IV) on War on Land and its Annexed Regulations on May 10, 1917.
(3) Territory is a form of property. A definition of "property" is given as follows.
Property: (1) something, as land and assets, legally possessed, (2) a piece of real estate, (3) something tangible or intangible to which its owner has legal title, (4) the right of ownership; title.
(4) Starr Memorandum, US Department of State. Memorandum from the Assistant Legal Adviser for East Asia and the Pacific (L/EA - Robert I. Starr) to the Director of the Office of Republic of China Affairs (Charles T. Sylvester), July 13, 1971. Subject: "Legal Status of Taiwan."
(5) The Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States is a treaty which was signed at Montevideo, Uruguay, on December 26, 1933, during the Seventh International Conference of American States. The Convention codifies the declarative theory of statehood as accepted as part of customary international law. The Convention became operative on December 26, 1934. It was registered in the League of Nations Treaty Series on January 8, 1936.
See -- https://www.taiwandocuments.net/montevideo01.htm
(6) A definition of "organic law" is given as follows.
Organic Law: A Constitution (or Charter) which organizes the juridical person called a state or country; similar to the Articles of Incorporation for a corporation to become a legal person or juridical person; the body of laws (as in a Constitution or Charter) that form the original foundation of a government; or one of the laws that make up such a body of laws.




